This post is the third in an occasional series in which I describe the making of a photograph, from both a technical and artistic standpoint. I’ll go through the camera settings and why they were chosen, as well as the thought processes going through my head regarding composition and the creation of the image. These types of posts will be concrete examples of a previous post of mine called How Pros Photograph, which describes the various decisions that may be going through a photographer’s head as they work a scene and make photos. The first post in this series can be read here, and the second post is here.
This one can be called the Aperture Edition or Depth of Field Edition, as you will learn below.

Men on Avenida el Sol – Cusco, Peru – 2008
The Photo: The photo I’ve selected for this example (seen just above) is one I took in Cusco, Peru in June 2008, called Men on Avenida el Sol. It was taken during the Cusco Week festivities, which is a series of events, dances, parades, and performances leading up to Inti Raymi, the Inca Festival of the Sun that occurs each year at the solstice. The wonderful thing about this week of activities is that it offers so many opportunities for a photographer to capture cultural, dance, and people photos. And because they are all public events where people expect, and even enjoy being photographed, it eliminates the difficulties and hesitations many photographers have about approaching individuals for photographs – although that is something any serious photographer needs to overcome, and it is actually quite easy. You approach the subject, make direct eye contact, and ask, “Do you mind if I take a photograph of you?” If they speak another language, hold up and nod towards your camera with a cheerful, inquisitive look on your face. They will either agree or not – problem solved!
Although I took hundreds of photos of the events over the week, I selected this one for this exercise because I learned something very definitively in the process of capturing it. More on that later. Although great subjects and action are directly in front of you during a parade or performance, there is a bit more to capturing good photos than just clicking away. I write a bit about that, with some tips and suggestions, in this post Cambridge Carnival.
This particular event was a parade down a main street of Cusco leading into the central plaza. I’ve created some strips of photos to show a selection of images as I worked this scene:
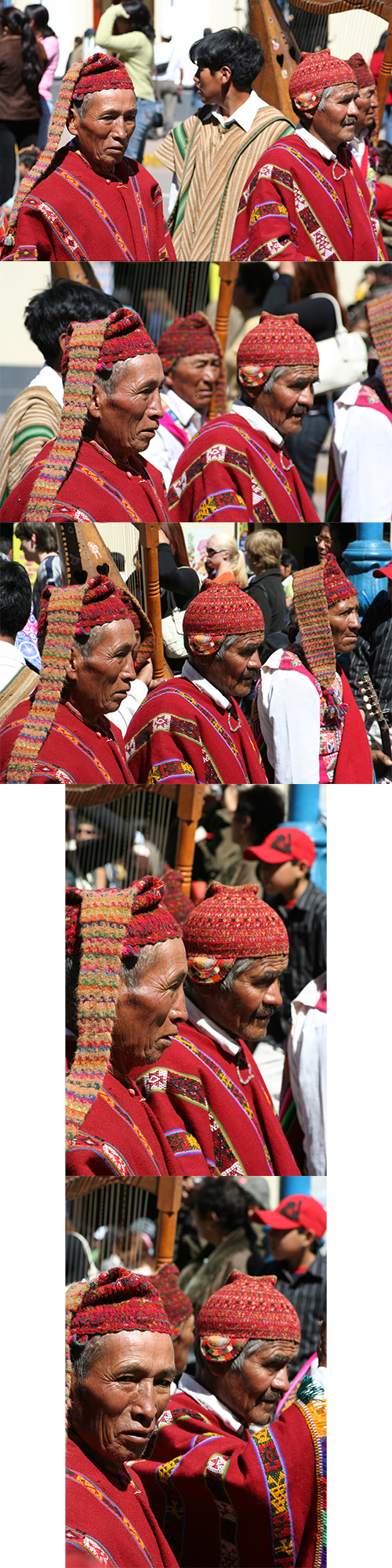

The Process: I was heading back home after taking dance photos in the plaza, and made my way down Avenida el Sol looking for additional quick shots. Most of the people and groups were standing about, waiting to move forward to perform or parade through the plaza, where the spectators were, so there were not many interesting opportunities. However, this group of older men captured my attention due to their wonderful expressive faces and their colorful traditional outfits. My intention was merely to capture these faces and subjects. However, they were a bit bored, just standing around waiting, so you can see most of the images do not really stand out.
I was using a Canon Rebel XT with a 28-105mm f/3.5-4.5 II lens. I stood on the sidewalk near the group, and set my camera on Aperture Priority mode (Av on Canon, A on Nikon). This was so I could control the depth of field and call attention to single or multiple subjects and make the background a bit blurry and less distracting. I experimented with various aperture settings, ranging from f/4.5 to f/13 depending on if I wanted one of the men to be in focus or a row of two or three of them to be in focus. A wide open aperture such as f/4.5 will have a narrow depth of field so that just one of the men is in focus, where a narrower aperture such as f/8 or f/11 will have a deeper depth of field so that the entire row of men might be in focus. With the wide apertures, I focused on the eyes of the man I wanted in-focus, and with narrower apertures, I focused about 1/3 or 1/2 way into the area I wanted to be in focus, meaning if there was a row of three faces, I focused on the middle one. The ISO was set at 200 which allowed the camera to choose fast shutter speeds of around 1/1000 s. This is because I had been capturing dance and action scenes, and wanted to be ready for the same. The metering mode was set on the general Evaluative Metering, which did a decent job of capturing the proper exposures. A couple images were mysteriously overexposed, possibly due to where I locked exposure while I was locking focus – which is why I now use a back-button focusing technique and/or lock exposures separately from focus. White Balance was set on Auto, but would have worked on Sunny as well.
As you hopefully know by now, depth of field is controlled by the aperture setting. I write more about it in these posts Depth of Field Simplified and Mastering Depth of Field. Since your specific depth of field in any situation will vary based not only on the aperture setting but also on the lens focal length and your distance from the subject, it is often difficult to predetermine what exactly is going to be in focus in the resulting image. You can try using the depth of field preview button on your camera, but it is difficult to see in the tiny, dim viewfinder what the preview is showing. You can also use your rear LCD and trial and error to view a series of experiments. But again, this is only a small screen with relatively low resolution, so it is difficult to see the precise results. And in many situations you simply don’t have the time for these methods. You just have to get a feel for your lenses and their different apertures through experience and studying your results. But one thing is certain: to get minimum, shallow depth of field and thus maximum background blurriness with any lens, zoom in as close as you can, (for example, zoom to 200mm on a 70-200mm lens) situate yourself as close as you can to your subject while still obtaining the framing you want, and use the widest aperture possible (for example f/2.8 or f/4). Work back from that if you wish to increase the depth of field – for example to have a slightly deeper depth of field in focus, use an aperture of f/5 or f/5.6, or increase your distance away from the subject, or remain close but use a shorter focal length like 28mm or 50mm.
As you can see, most of the images are very “busy,” with a lot of extraneous and distracting background people and activity. I wasn’t very pleased with the images, but I continued to take basically the same image over and over. I knew the faces, outfits, and colors were interesting, and I hoped the resulting images would be as well. I zoomed in as close as I could with most of the images, working in the 75mm to 105mm range of my lens. However, without a lens that had the 100mm to 200mm range, I could not zoom closer and could not obtain the “compression” I was looking for, where the more distant faces would appear to be closer behind the closest subject.
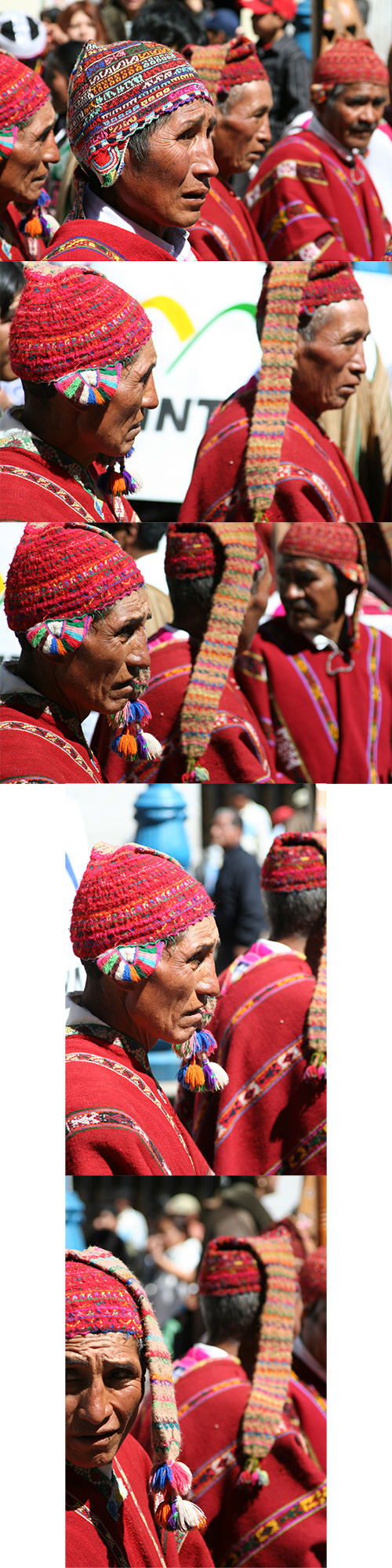

What I didn’t do that I should have been doing, instead of trying to take the same photo over and over, was to change my position and point of view. Doing so would change the backgrounds, perhaps make them less busy or distracting (such as the spectators and the white sign), and would allow for the camera to be on the same level or looking up towards the subjects rather than looking slightly down at them.
I took a series of 60 images over a period of 7.5 minutes. Besides the selected image, only a couple other ones are mildly interesting. I knew I wasn’t capturing what I wanted, my companion was becoming impatient, and eventually I decided to move on. But then I took a few final images. My point of view had slightly changed. I was directly to the side of the men and slightly closer. The last image finally got what I had wanted. It stands out dramatically among all the other ones. It is more simple and straightforward, less cluttered, and the subjects fill the frame.
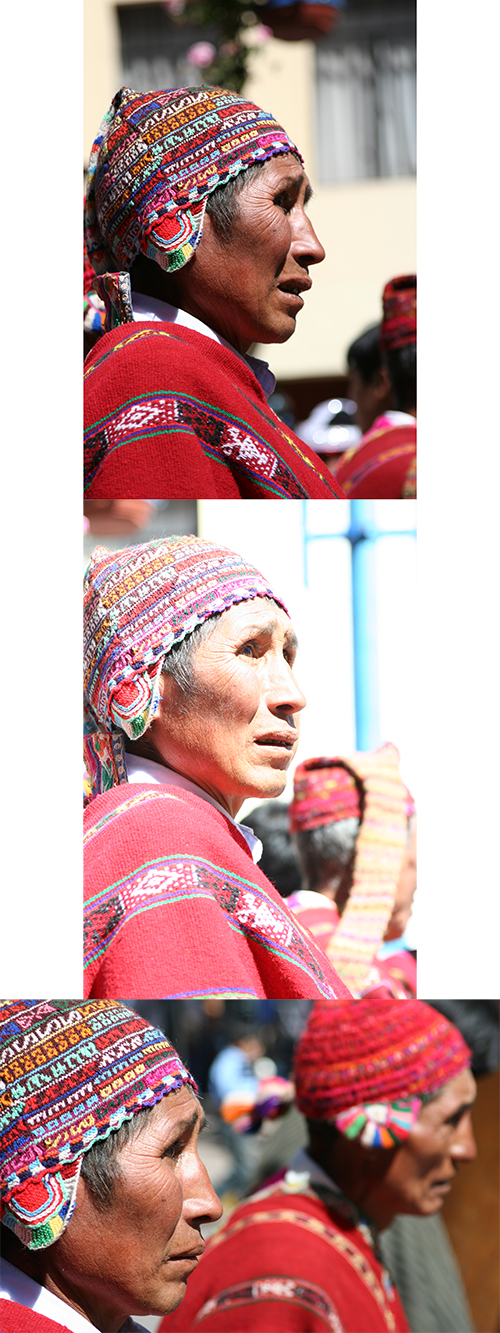

The Post Process: To create the final image, I adjusted the color and contrast in Adobe Camera Raw (ACR) and in Photoshop (PS). As you can see by the unprocessed images, the color and contrast is a little dull and lifeless straight out of the camera. The original file was a JPEG file, and the Picture Style was Standard (I hadn’t started using RAW yet). In ACR, the Blacks were increased to about 7 or 10 to give it the nice deep blacks, which helps to make the bright colors pop even more. Some Recovery was used to bring back the overexposed highlights on the man’s face. Clarity and Vibrance were used to give it some, well, clarity and vibrance. In Photoshop, the contrast was increased with Curves using the preset setting of Linear Contrast. In Levels, the midtones were darkened to .93 to give a deeper more realistic color to the faces. I did some additional burning on the faces to try to reduce the hot-spots. The image was sharpened using Unsharpen Mask, probably at Amount: 85 or 100, Radius: 1, and Threshold: 4. I may have used the Hue/Saturation to reduce the saturation and lightness of the red color, though I should have done that a little more, as you can see by the man’s face which appears too red and the rear hat where the red is blown out. The Rebel XT sensor, and other digital SLR sensors often overexpose the color red. It is similar to blowing out the highlights, where the color red is blown out and there is just red and not other detail in those areas. You can use the RGB histogram rather than the brightness histogram to monitor for this on the camera’s rear LCD screen while reviewing images. I didn’t crop the image at all, as you can see. It is best to try to get the framing you want when you capture the photo, especially when using an 8 megapixel camera that doesn’t allow for much cropping! (A cropped image would have much lower image quality because the resulting resolution would be much less – it would not allow for much manipulation, and would appear pixellated when enlarged.)
The Final Image:

Canon Rebel XT, 28-105mm f/3.5-4.5 II at 93mm, ISO 200, f/5, 1/1000s
The Lesson: We should always learn from our photos, so that next time we are in a similar situation, we can create an even better image. The valuable lesson I learned in this situation, in addition to perhaps always grabbing one final frame, is to make a change when the composition is not working. Change your perspective, angle, or point of view. Zoom in or out to change the framing. Don’t continue to take the same image that isn’t working, over and over again. If the subject is interesting, there is an interesting composition that can be found to best express that subject. Mentally envision the scene from a variety of positions and angles, and move around the scene as much as possible to see the options. Some other improvements I could have made to this image include using a polarizing filter. Because I was working in the bright, harsh mid-day sun at a high altitude, this could have improved the exposure, color rendition, and contrast of the original image. Since it was overexposed a bit, causing hot-spots on the subject’s face, I should have paid more attention to my histogram and adjusted the exposure compensation accordingly, or used a different metering mode such as Partial or Spot to meter directly off the man’s face.
So hopefully you can see from this explanation and from my previous posts that photographs don’t necessarily just happen. They are created through a combination of thought processes, a series of decisions, and the application of camera settings based on these decisions and on the situation at hand.
See the Related Posts section just below for links to parts 1 and 2 in this series. And learn more about how to take control of your camera and the images you create with my Full Stop e-book camera and photography guides.