I’ve been waiting until I got my hands on the latest new dSLR, so that I could coordinate a camera “field test” with a visit to an exhibit I’ve been wanting to see. The Heritage Museum and Gardens is currently showing an exhibit of concept cars, called Driving Our Dreams, which will be there until October 27, 2013. They have gathered together one of the coolest collections of American concept cars from the 1950’s to the present, ranging from the “space-age” 1956 GM Firebird II turbine powered highway rocket to the solar powered 2009 Infinium – and what better place to try out a new camera?! So thanks to LensProToGo for putting a new Canon EOS 70D into my hands, just as it was hitting the stores at the end of August!

All images in this post taken with the Canon 70D at the Heritage Museum, Sandwich, Massachusetts. 1956 Buick Centurion concept car. (Learn about the over-saturated red channel below.)
I headed out to Sandwich, Mass., the oldest town on Cape Cod, to visit the museum. I’ve been researching and writing about the 70D since it was announced a few months ago, as I work on my latest camera guide Canon 70D Experience, so I was already extremely familiar with its features and controls.
You can read all about the camera’s new features, and some tips for customizing the settings and controls of your 70D, in some of my previous Canon 70D articles. And if you wish to learn not only the features, functions, and controls of the 70D, but more importantly when and why to use them, be sure to look at my guide Canon 70D Experience. It will help you to take control of your camera, and the images you create!

Controls and Touch Screen: If you have worked with a Canon 60D, 7D, or even a 50D (or earlier), you should find that the 70D feels very familiar. It has about the same weight and feel, and while some of the controls move around from model to model, most of them are similar. I found that I quickly learned which button to instinctively press for my needs, whether the Image Playback Button, Info Button, or Q Button, etc. Even more convenient is the new Touch Screen, first seen on the Canon Rebel T4i/ EOS 650D. For those who may be skeptical about using a touch screen because of either responsiveness concerns or due to the “purity” of using a camera’s controls, the Canon 70D Touch Screen may very well change your mind. As with the screen on the T4i/650D and T5i/700D, it is as responsive as you have come to expect with an iPhone, and even uses many of the same Multi-Touch gestures – particularly when reviewing images during Image Playback (swipe for the next image, spread and pinch for zooming in and out, etc.). Even though many of the menu tabs, menu items, and function icons of the 70D are tiny, I rarely ever have any problem immediately selecting the right one. And regarding the desire to use the actual camera buttons and controls to change settings, I have quickly gotten into the habit of just pressing the Q Button to access the Quick Control Screen, then using the Touch Screen to change my settings with a few taps. After I have reviewed an image and wish to change settings, I find that it is quicker and easier to do it this way and simply leave the camera in the same position in your hands as you look at the rear screen, than it is to tilt the camera up, locate your desired settings button, press it and look at the small top LCD screen. You can change all the shooting settings on the Quick Control Screen, jump around the menus for various other settings, review all your settings on the Shooting Function Settings screen, and go back into image review all with your right thumb and left index finger, while holding the camera in the same position. Though I still use the dials and controls to change the aperture / shutter speed settings and control the autofocus points as I work through the viewfinder.

1954 Buick Wildcat II concept car
The top Main Dial of the 70D, while solid, has that great “soft” rubber feel to it rather than the harder plastic feel of entry-level models. And this softer material is much easier on your fingertip after a long day of shooting. I always gripe about the inclusion of the thumb-pad Multi-Controller on the 60D and 70D, rather than the joystick version of the 7D, 50D, and 5D Mark III. I prefer the joystick because of its location, which is much closer to the other buttons on the top rear of the camera that your thumb will also be using. However, I found that after some time with the 70D I eventually got used to the thumb-pad. While I still dislike the location, it does make it a bit easier to select an autofocus point the diagonal directions. One of the Custom Controls that I found I like is to customize the SET Button for ISO selection. While there is a dedicated ISO Button on the top of the camera, or you can easily select it on the Quick Control Screen, I find that it is also quick and easy to press the SET Button as you turn the top Main Dial to make this adjustment. As described above, it helps you to make this adjustment while keeping the camera in the same “image review” position. Plus you can quickly use this method to change the setting while your eye stays in the Viewfinder. And while you can always use the top ISO button in the same manner, it is much more difficult to determine which top button is the ISO Button without looking at it. (While it has a little bump on it to help locate it by feel, it is not a big enough difference from the other buttons for me to locate it with confidence.)

1962 Corvette – production model
I decided with this photo shoot to use the 70D just as I would during any normal shoot, and thus concentrate on the controls, exposure issues, and autofocus system (rather than, say, playing with the Multiple Exposure or HDR features). I had earlier experimented with some of the other functions of the camera such as Auto Lighting Optimizer, in-camera HDR, Multi-Shot Noise Reduction, Multiple Exposures, Creative Filters, etc., and those can all be learned about in Canon 70D Experience. There will also be example images of all these features in my Canon 70D Flickr set.
Lighting, Exposure, White Balance, and Noise: One of the first things I discovered is that lighting at an indoor automobile exhibit is very challenging! While they allowed the use of flash, it would not have worked out well due to all the reflections and bright spots it would cause in the car body, glass, and chrome (which of course is well represented in the 50’s cars). Perhaps indirect flash would work well, but as I was going to be taking hundreds of shots, I didn’t wish to disrupt the other visitors with constant flashes. In addition, getting the right exposure was challenging because I was often taking close-up shots of a large area of a light tone or dark tone, which would fool the exposure meter and cause it to want to under- or over-expose the image. Plus some of the cars were bare metal, which is prone to very bright reflective areas and dark non-reflective areas depending on how the lights are hitting it and the angle of view. So the exposure level reading could change dramatically from the initial framing where I locked focus to the final framing when I took the shot. I had to carefully keep an eye on how the light changed based on what area of the car I was photographing, as well as how it changed based on my angle of view as I moved slightly side to side, or crouched down low. I needed to sometimes lock the exposure settings for my final framing or for an important area (using the AE Lock * Button on the rear of the camera), and I had to check the results and the histogram, and adjust the Exposure Compensation to lighten or darken the subsequent shots (while then remembering to set EC back to 0 when I moved on to the next shot!). (If you don’t yet fully understand what this all means, I discuss locking exposure settings, the Histogram, and Exposure Compensation in detail in my Canon 70D Experience guide.)

1962 Corvette – production model
There was relatively low lighting in the exhibition space, but I was able to make use of ISO 1600. I primarily worked in Aperture-Priority AE Shooting Mode (Av) so that I had control of the depth of field. Sometimes the shutter speed that the camera chose dropped below a desirable 1/100 or 1/125, so I often took a quick burst of images knowing that at least one would come out sharp. In truth, I just looked over my previous ISO tests of the 70D, and there is very little loss of quality between 1600 ISO and 3200 ISO, in the JPEG images straight from the camera. Some excessive graininess definitely appear by 6400 ISO. So I could have safely increased the ISO well above 1600, perhaps even up to 3200. But it was simply an old habit of never going above 1600, drilled into me with older cameras such as the 50D – and I should have left that prejudice aside when working with the 70D. You can view JPEG test results at the various ISO settings, in my Canon 70D ISO Flickr set.
The images shown here and on Flickr were originally shot in RAW image quality, and converted to DNG using the Adobe DNG converter. They were then processed, sharpened, and saved as JPEG. Unfortunately, I did not apply any noise reduction during processing, and the results are excessively noisy. I am going to have to go back and apply noise reduction to these images, either using Photoshop or Canon Digital Photo Professional (DPP). Below are some details of the above image, showing the difference between:
- the original JPEG
- the original RAW converted with Adobe DNG and processed in Photoshop and output as a JEPG, no noise reduction
- the original RAW processed in Canon DPP with noise reduction applied and output as a JPEG.
For any pixel peepers, please note that all of the processing was done relatively quickly, so as to illustrate the overall differences. This is not intended to show definitive lab-quality results that one could achieve with much more careful, patient processing and noise reduction application. Please view the results at DPReview to see their lab-quality tests of JPEG, RAW, image quality, and noise.
Click on these image details to see larger versions:

Detail of original JPEG straight from camera, 1600 ISO with “High ISO Speed NR” set for Standard – very little noise seen.

Detail of processed RAW>DNG (processed with Photoshop)>JPEG, with no noise reduction applied, and thus excessively noisy.

Detail of processed RAW (processed with Canon DPP)>JPEG with noise reduction applied, very little noise seen.
So the lesson of the above examples is that you can confidently shoot in JPEG, up to 1600 and even higher, and achieve clean, low-noise results. You can make use of the 70D in-camera High ISO Speed NR option to assist with this, setting it for Standard or High. View the tests on DPReview to see how high you are willing to raise the ISO before the noise is too much for your tastes or image-output needs. And, if you shoot in RAW, you are going to need to apply noise reduction (and contrast, sharpening, etc. as always) as you process the images, especially when you are shooting in high ISO settings (800, 1600, and higher). Apply noise reduction in Adobe Camera Raw, Photoshop, Lightroom, Aperture, Canon DPP, etc.
Regarding White Balance, I learned that I should not have forgotten to bring my digital grey card for creating some benchmark images or even for setting a Custom White Balance. Though my post-processing experiments, I discovered that the White Balance color temperature of the exhibit space was very close to the Incandescent setting, but it would have been helpful, and would have saved time, if I had simply taken a couple images with the grey card in the scene. The lighting also varied throughout the space, as some areas had a bit of daylight from large windows. With images like these, I feel it is very important to closely match the actual colors of the cars, as they are documentary images of sorts. While the artificial lighting of an exhibition space vs. natural lighting outside would make these cars, (and images of these cars) appear differently, I wanted to match as closely as possible what I saw. If you wish to create a Custom White Balance with the 70D, you can take an image of a white object or grey card, filling a large central area of the Viewfinder with the card (about the size of the AF Points diamond), then go into the Shooting 3 menu and select the Custom White Balance menu item. It will ask you to select the image of the grey card you just took. When that is set, simply set your White Balance setting to the Custom WB icon, by pressing the Q Button and using the Quick Control Screen.

1956 Buick Centurion concept car
As is common with many dSLR sensors, the red channel can have a tendency to be sensitive to over-saturation. I experienced this as well with the 70D, though as you can see in the above image there was a large expanse of brightly lit red. In this and other images of the red and white Buick Centurion, some of the brightest areas of red become over-saturated and lose all detail, variation, or shadow, and are simply “pure” red. This is most easily seen in the first image at the top of this post, where there is a large area of lighter red on the top of the rear fender, where all subtle detail of varying color tones and shadow gradation is lost. If you are only watching the Brightness Histogram you may not pick this up, as the overall image – according to the camera – is not over-exposed. In order to keep your eye on this as you work, you can make use of the RGB Histogram. As shown below, the red channel is cut off at the right edge of the graph, and thus all detail will be lost in those areas of the image where this occurs. The sensor has simply reached its limits of what it can capture. If you experience this, you can adjust the lighting and perhaps make use of reflectors or diffusers, or move the subject, or alter your angle of view. In a situation where you can’t control these elements, you will need to adjust the exposure (under expose) before retaking the image, then check the RGB Histogram to make sure the color channels are not cut off at the right side of the graph. Then carefully work with the image in post-processing to “bring back” or raise the overall exposure while trying to keep the problematic color channel from becoming over-saturated.
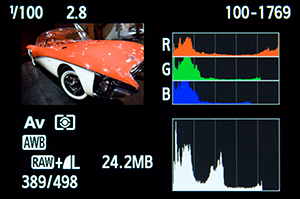
Canon 70D RGB and Brightness Histogram, showing that areas of red have been over-saturated.
Aperture-Priority, Lenses, Autofocusing: As I mentioned above, I primarily worked in Aperture-Priority AE Shooting Mode, where I controlled the aperture setting while the camera chose the appropriate shutter speed. This allowed me to control the depth of field of the images, since I was primarily aiming to achieve very shallow, dramatic depth of field in the detail images, as shown in the tail-fin image below:

1954 Buick Wildcat II concept car
By working with a Canon 70-200mm F/4L IS lens, I set the lens at or near the 200mm focal length, backed up several yards, and then focused on my area of interest while setting the aperture at f/4. This results in very shallow depth of field and calls attention to the area of detail. For the images showing a larger area of the cars, I used either the 16-35mm f/2.8L wide angle lens or the Canon 24-70mm f/2.8L, with the aperture set around f/2.8 or f/4.
I primarily autofocused using One-Shot AF Focus Mode and Single-Point AF Autofocus Area Selection Mode. One-Shot AF is used for still (or relatively still) subjects. As with the Canon 7D, the 70D has an Autofocus Area Selection Button on the top of the camera near the Shutter Button, which allows you to choose between these modes as you look through the Viewfinder (Single-Point AF, Zone AF, or 19-Point Automatic Selection AF), and these modes determine how many AF Points are being used to try to find the subject to focus on. With Single Point AF, I am able to manually select my desired AF Point using the Multi-Controller as I look through the Viewfinder, place it over the exact area where I wish to focus, and then lock focus with a half-press of the Shutter Button or by pressing the rear AF-ON Button. I can then recompose the shot to get the framing I desire, and press the Shutter Button to take the shot. While the 70D has 19 AF Points to choose from, it is relatively quick and easy to select the one you wish. You can even customize the camera so that if you are selecting one of the edge points, you can choose to stop at the edge or “wrap-around” to the AF Point on the other side if you continue to click the Multi-Controller. I always choose to have it stop at the edge. That way if I am choosing an “edge” point, I can simply quickly “click, click, click” on the left Multi-Controller, and I know it will stop at the far left AF Point and not “wrap-around” to an AF Point on the other side of the frame.
As you may be aware, the Canon 70D has a brand new, potentially revolutionary Live View / Movie autofocus system. It is a phase-detection AF system called Dual Pixel CMOS AF, which can quickly and smoothly grab focus, and can also be used to very effectively track a moving subject. Based on my tests and on many test videos found on the Internet, the system is living up to the hype and performs as well as promised. Previously, Live View focus was slow, and the camera often hunted for the subject. With this new system, it achieves focus on the subject extremely quickly an accurately. I made use of both the rotating rear LCD screen of the 70D and the Live View AF system to take some shots looking down from the first level onto the lower level, as seen in this image:

1956 GM Firebird II concept car
I held the camera out at arms length, rotated the rear screen so that I could see it, and pressed the AF-ON Button to lock focus. Even in the low lighting, the camera immediately focused. With the Live View autofocusing system you can also select from different autofocusing methods that determine how large an area the camera looks at to find a subject. Again I used the smallest, most precise area, called FlexiZone-Single AF, which provides a small focus square that you can move around the screen and locate where you wish, either using the Multi-Controller or the Touch Screen.
Creative Filters: In spite of what I said earlier, I did play around with the in-camera Creative Filters and applied them to some of these images. I used the the Art Bold Effect, which affects contrast and saturation, on an image of the Buick Centurion. By setting it on the High setting, I totally blew out the red (over-exposed), but is also made the interior glow nicely and has a cool effect on the chrome. And I used the Fish-eye Effect on the Buick Wildcat II, which works well if you get in close while having receding lines, as I found at the corner of this bumper.

Canon 70D In-camera Creative Filter – Art Bold Effect – High.

Canon 70D In-camera Creative Filter – Fish-eye Effect – Low.
Conclusion: After spending a dedicated week with the Canon 70D, exploring every menu item and experimenting with every function and feature, I have grown tremendously fond of this camera. Part of this is the familiarity I feel from working so long with the 50D and the 7D. But it is also due to some of its new features, which would make going back to either of those cameras extremely difficult. The first is the Touch Screen, which is an extremely quick, easy, and convenient way to change settings on the fly, access menus, and review images. Second is the new Live View autofocus system, which works as well as promised. It mot only makes Live View shooting much less frustrating and much more viable for all kinds of shooting situations, but it also makes autofocusing during movie shooting a reality. In addition, you can now use the Touch Screen to immediately change the area of focus, while movie shooting, simply by touching the screen. And finally, there are some of the smaller features, but these little additions can make a big difference. For example, during image playback you can access the Playback Quick Control screen and quickly set an image Rating. When this first appeared on the 5DIII and Rebels, I thought it might be a bit frivolous. But I have come to make very effective use of it, and will miss it on other dSLRs that don’t have this feature. It allows you to go through your images and the camera and quickly mark (rate) the best ones, as well as mark the bad ones (with one star) that you will likely be able to quickly delete after viewing them on your computer. It is a simple feature that can provide significant time savings in a busy workflow.
Another simple feature that I discovered I made use of more than expected is the electronic level in the viewfinder. Unlike previous cameras where you can use the AF Points, as seen in the Viewfinder, as a level, the 70D includes a small “level” icon at the bottom of the Viewfinder screen. (You can also make use of the AF Points as a level, which is sort of a hidden feature I will explain in a moment.) This level icon is simply a camera icon surrounded by either straight or diagonal lines, which indicate if you are on or off level. Or if both the straight and diagonal lines are displayed, you are almost level. I have long had a tendency to hold the camera slightly off-level, so I always appreciate the Viewfinder grid, which can be enabled in the 70D. But this level icon helped even more to keep my images straight. I found that I could compose the image, take care of locking focus and exposure if necessary, and then take a peek at the level icon before pressing the Shutter Button to take the shot. More often than not, it indicated I was slightly off, so I carefully leveled the camera and took the shot. Again, such a simple feature helped a great deal – by keeping my images straight and level, which eliminated the need to straighten (and thus slightly crop) numerous photos later in Photoshop.
Regarding the “hidden” Viewfinder level that uses the AF Points, you can use the Custom Controls to set the Depth of Field Preview Button to the Electronic Level option. You can then press this DOF Preview Button during shooting and activate a level that uses the AF Points in the Viewfinder to indicate if the camera is level or not. Press the Shutter Button to turn it off and return to shooting. You can learn about several other Custom Controls and Custom Function settings in my post on the 70D Custom Controls.

1956 Buick Centurion concept car
Regarding image quality, while I failed to properly apply noise reduction to the RAW images used here as I processed them, my subsequent tests and inspections have confirmed that you can work in high ISO settings (approaching 3200) and achieve a low, acceptable amount of noise with JPEG images straight out of the camera, and with RAW images with noise reduction applied in post processing. This has been confirmed with test images on DPReview and other sites.
Additional concept cars and more images from this visit to the Heritage Museum can be seen on Flickr here.
Remember to check out my other Canon 70D blog posts to find out more about the camera. And if you wish to take control of your Canon 70D, and learn how, when, and why to use its controls, features, and settings, be sure to check out my e-book guide, Canon 70D Experience.
If you are planning to purchase your Canon 70D online, please consider using my affiliate links and help support this blog – thanks!
Order your Canon EOS 70D from Amazon or B and H Photo:
Amazon:
Canon 70D – Body or with choice of kit lenses – $1,199 to $1,549
B and H Photo:
Canon 70D – Body only – $1,199
Canon 70D – with 18-135mm STM lens – $1,549
Canon 70D – with 18-55mm STM lens – $1,349
~ ~ ~
Was this post helpful? Please let others know about it by clicking the Facebook or Twitter sharing buttons below, linking to it from your blog or website, or mentioning it on a forum. Thanks! Want to help support this blog with no cost or effort? Simply click on the Amazon, B&H Photo, or Adorama logos on the left side of this page to go to those sites and make your purchases. They will then give me a little referral bonus!